Texas, a state known for its vast landscapes and rich cultural heritage, has a distinct political climate shaped by its primary election systems. Understanding the types of primary systems employed in Texas is essential for anyone looking to navigate the state’s political landscape. These systems dictate how political parties select their candidates for the general elections, significantly impacting the electoral process.
Texas primarily utilizes a semi-open primary system, which allows registered voters to participate in either party’s primary election without being required to be a member of that party. This unique feature fosters a diverse electorate, inviting independent voters to engage in the primary process. It presents an opportunity for political parties to attract a broader base by allowing voters to choose which primary to participate in, irrespective of their registered party affiliation.
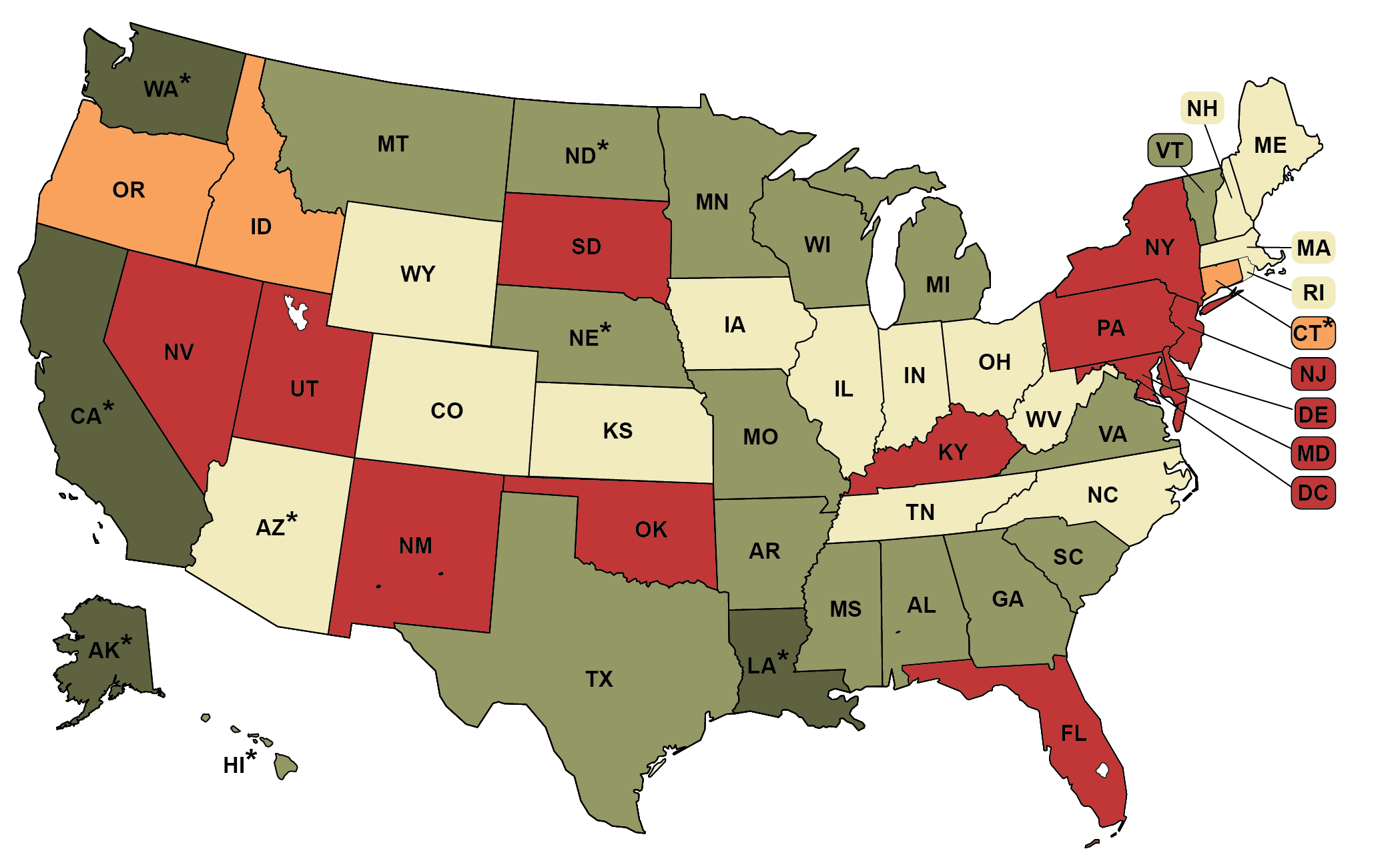
Additionally, the Texas primary system has elements of both open and closed primaries. While voters can switch parties, they must declare their chosen party on the day of the primary. This decision can shape the outcome of elections, as it allows for strategic voting—where voters might choose to participate in the primary of a party they do not primarily support if they believe their intervention can influence the final candidate selection.
However, it’s important to note that while participation is open, the political party must still adhere to its own rules regarding membership and candidate selection processes. After the primary elections, the state’s political landscape gets further shaped by runoff primaries, which occur when no candidate achieves the required majority of votes. This aspect of the system ensures that candidates must secure strong support within their party, which can often lead to more centrist or broadly appealing candidates being selected for the general election.
Moreover, Texas is noteworthy for its early primary date within the election cycle, typically held on the first Tuesday in March. This positioning grants it a critical role in national elections, often seen as a bellwether for the political sentiments of the nation. Candidates and parties aim to secure early momentum in Texas, making it a focal point for campaign efforts and strategies.
Voter engagement is another vital aspect related to Texas’s primary election system. The semi-open nature of its primaries encourages voter turnout, as individuals feel empowered to vote in a manner that reflects their true preferences without the constraints of party identity. This aspect can lead to increased participation and a more representative electoral process.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain within Texas’s primary system. Voter turnout can be inconsistent, typically lower than in general elections. Moreover, the state has faced scrutiny over voter registration laws and access, with advocates calling for reforms to ensure that all eligible voters can easily participate in the primary process. This ongoing debate highlights the need for transparency and accessibility within the electoral system.
In summarizing the primary election systems active in Texas, it is evident that the semi-open primary model plays a significant role in shaping the state’s political dynamics. By allowing registered voters flexibility in their participation while still adhering to specific party rules, Texas cultivates a unique environment for political engagement. The implications of this system extend beyond state lines, influencing national trends and voter behavior.
As Texas continues to evolve politically, understanding its primary election system is crucial for anyone interested in the state’s political affairs. This knowledge not only aids in grasping the electoral process but also provides insights into the broader implications of voter engagement and party dynamics. Whether you’re a seasoned political observer or a newcomer to Texas’s vibrant political scene, staying informed about these systems is essential for meaningful participation in democracy.