Edamame Seeds for Planting: A Guide to Growing Your Own Soybeans
Edamame, the young green soybeans, have gained immense popularity not only for their delicious taste but also for their nutritional benefits. As more people become interested in gardening and sustainable living, the idea of growing edamame seeds for planting has captured the attention of many. This article explores the essential aspects of cultivating edamame, from selecting the right seeds to harvesting the beans, ensuring a rewarding gardening experience.

When considering edamame seeds for planting, the first step is to choose high-quality seeds. Look for seeds that are specifically labeled as edamame, as these varieties are bred for their tender pods and sweet flavor. Popular cultivars include ‘Hokkaido’ and ‘Midori Giant,’ which are known for their excellent taste and yield. Purchasing seeds from reputable suppliers ensures that you receive viable seeds that are free from diseases.
The ideal time to plant edamame seeds is during the warm months, typically after the last frost. Edamame thrives in temperatures between 70°F and 85°F (21°C to 29°C). Before planting, prepare the soil by ensuring it is well-drained and rich in organic matter. A pH level between 6.0 and 7.0 is optimal for growth. Adding compost or well-rotted manure can enhance soil fertility, providing the necessary nutrients for the plants.
When planting, space the seeds about 2 to 4 inches apart in rows that are 18 to 30 inches apart. This spacing allows for adequate air circulation and sunlight exposure, which are crucial for healthy growth. Cover the seeds with about 1 inch of soil and water them gently to avoid displacing the seeds. Consistent moisture is vital during the germination phase, which typically takes about 7 to 14 days.
As the plants grow, they will require regular care. Weeding is essential to prevent competition for nutrients and water. Mulching around the plants can help suppress weeds and retain soil moisture. Additionally, edamame plants benefit from a balanced fertilizer applied during the growing season. Look for fertilizers with a higher phosphorus content to promote flowering and pod development.
Pest management is another critical aspect of growing edamame. Common pests include aphids and spider mites, which can be controlled through natural methods such as introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs or using insecticidal soap. Regularly inspecting the plants for signs of pests or diseases will help maintain a healthy garden.
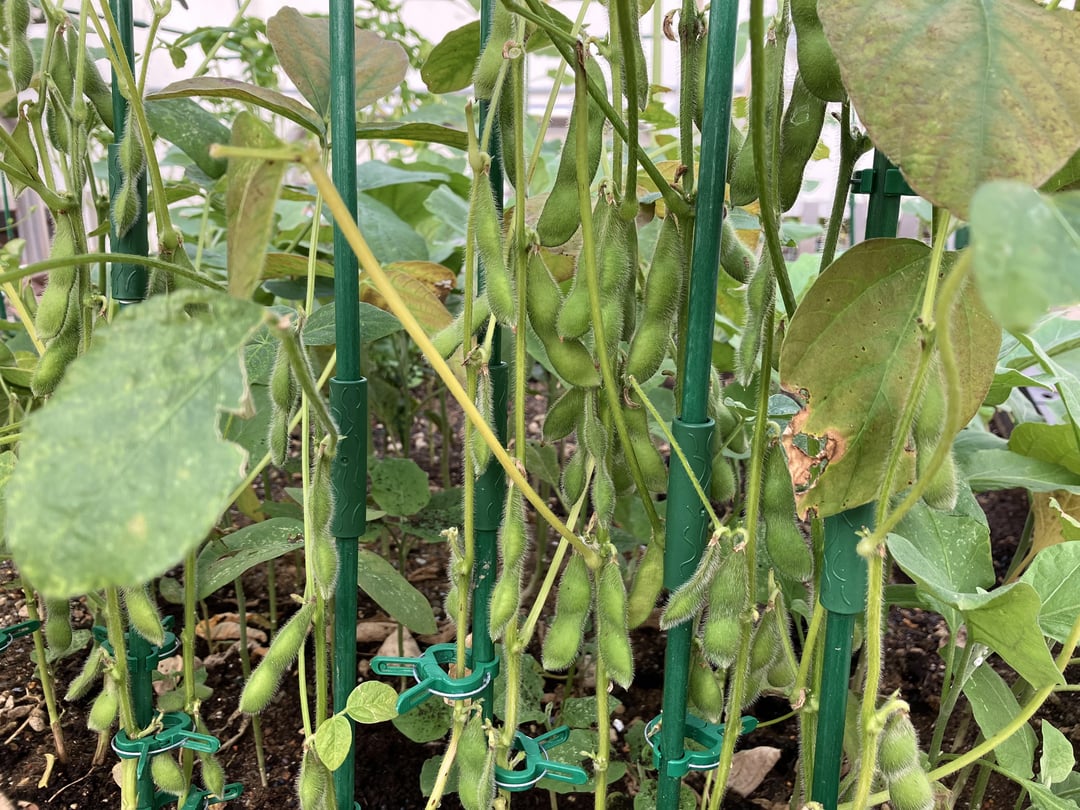
As the edamame plants mature, they will begin to produce pods. The ideal time to harvest is when the pods are bright green and firm, typically around 70 to 80 days after planting. Harvesting should be done by hand, gently pulling the pods from the plant. It is essential to pick the pods regularly to encourage further production.
After harvesting, the edamame can be enjoyed fresh, steamed, or blanched and frozen for later use. The nutritional benefits of edamame are significant; they are rich in protein, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals. Incorporating edamame into your diet can contribute to a healthy lifestyle.
Growing edamame seeds for planting not only provides a delicious and nutritious food source but also offers a fulfilling gardening experience. The process of nurturing the plants from seeds to harvest fosters a deeper connection with nature and promotes sustainable practices. Whether you have a large garden or a small balcony, cultivating edamame can be a rewarding endeavor that enhances your culinary repertoire and contributes to your well-being.

By understanding the requirements and care needed for edamame, anyone can successfully grow this delightful crop. With the right seeds, proper planting techniques, and attentive care, you can enjoy the satisfaction of harvesting your own edamame, bringing a taste of the garden to your table.