Doest Stereo Measurement Read Pit Depth
In the realm of modern surveying and measurement techniques, the quest for precision has led to the development of various methodologies. One such method that has gained traction is stereo measurement, which utilizes two or more perspectives to gather data about an object or surface. This technique has proven particularly useful in applications such as topography, architecture, and even in the analysis of geological features. A pertinent question arises: does stereo measurement effectively read pit depth?
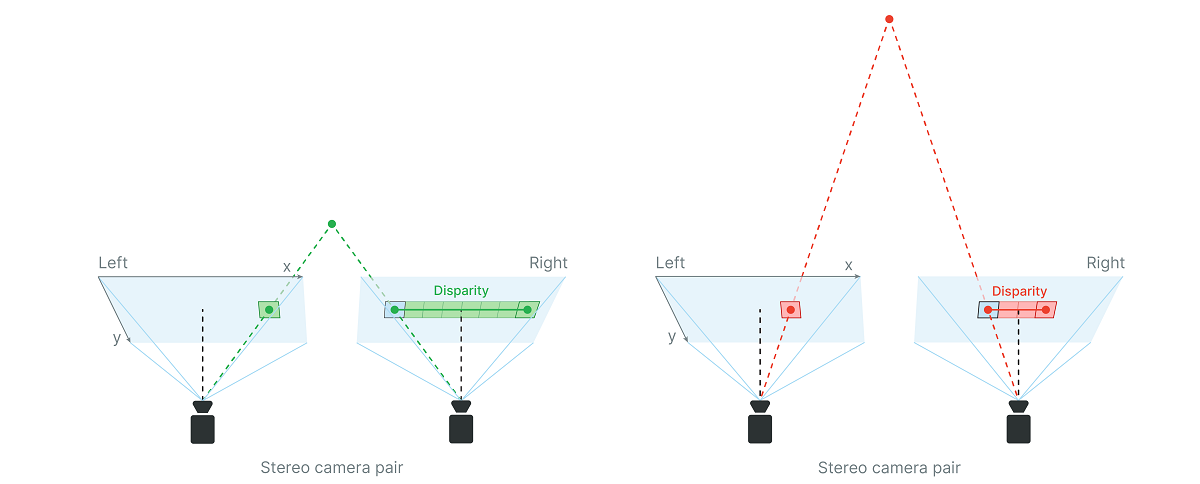
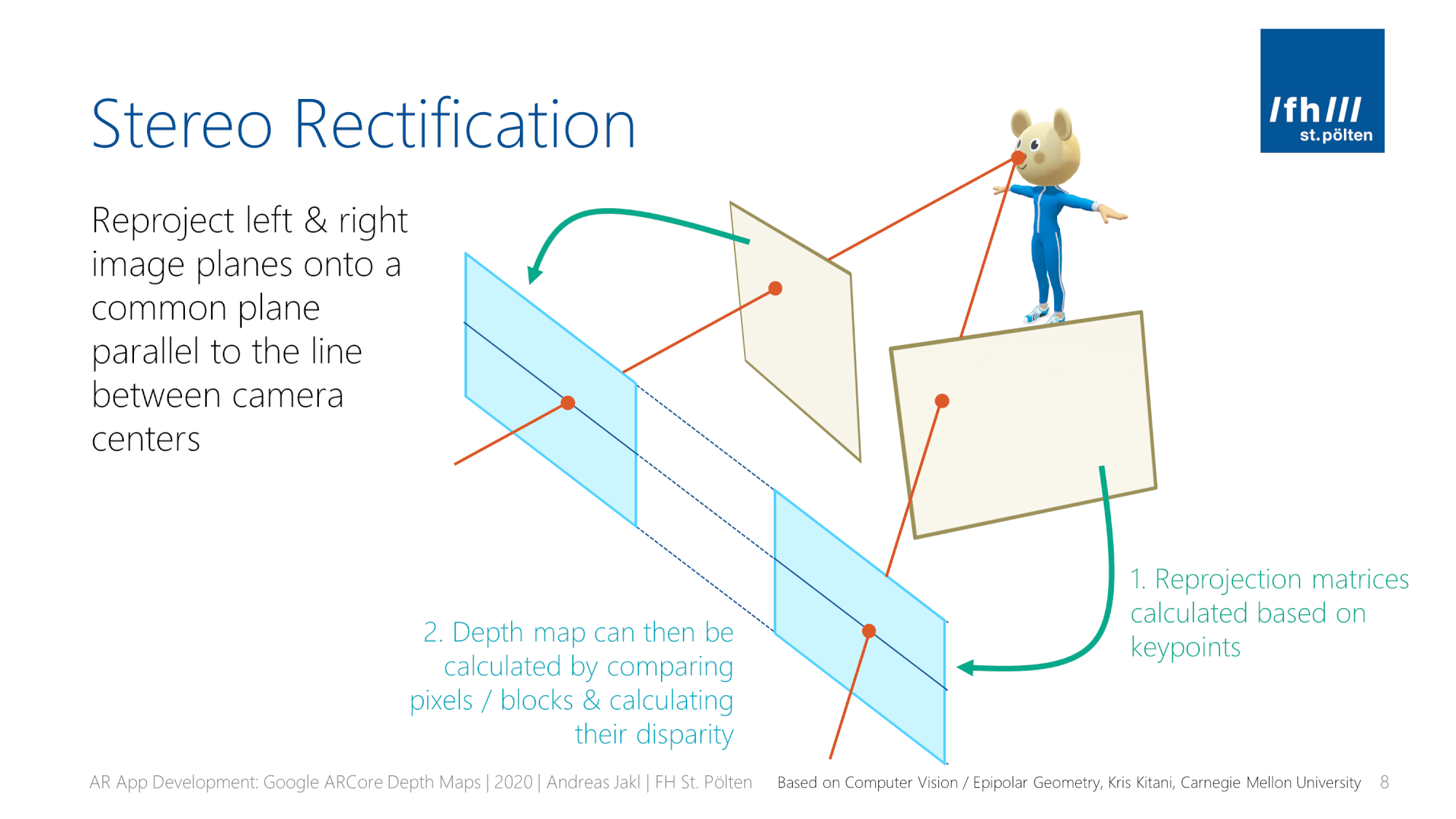
To understand this, it is essential to delve into the mechanics of stereo measurement. This technique operates on the principle of triangulation, where two or more images of the same object are captured from different angles. By analyzing the disparity between these images, it is possible to calculate the depth and dimensions of the object in question. This method is akin to how human vision perceives depth; our two eyes provide slightly different views, allowing our brain to interpret distance and depth accurately.
When applied to measuring pit depth, stereo measurement offers several advantages. Firstly, it allows for a more comprehensive view of the pit’s geometry. Traditional methods, such as single-point measurements or laser scanning, may miss critical features or variations in depth. Stereo measurement, by capturing multiple angles, can provide a more detailed and accurate representation of the pit’s profile. This is particularly important in mining and excavation, where understanding the exact depth and shape of a pit can influence operational decisions and safety protocols.
Moreover, stereo measurement can be integrated with advanced imaging technologies, such as drones equipped with high-resolution cameras. This integration enhances the ability to capture large areas quickly and efficiently. The data collected can then be processed using specialized software to generate three-dimensional models of the pit. These models not only depict the depth but also highlight other significant features, such as slopes and potential hazards.
However, the effectiveness of stereo measurement in reading pit depth is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the accuracy of the images captured. Factors such as lighting conditions, camera calibration, and the resolution of the images can significantly impact the quality of the depth readings. Inadequate lighting can lead to shadows and reflections that obscure details, while poorly calibrated cameras may introduce errors in the measurements. Therefore, ensuring optimal conditions for capturing images is crucial for achieving reliable results.
Another consideration is the complexity of the pit’s shape. Irregularities, such as overhangs or varying slopes, can complicate the stereo measurement process. In such cases, additional techniques may be required to supplement the stereo data. For instance, combining stereo measurement with ground-penetrating radar (GPR) can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the pit’s structure. GPR can penetrate the surface and reveal subsurface features that may not be visible through stereo imaging alone.
Despite these challenges, the potential of stereo measurement in accurately reading pit depth is significant. The ability to visualize and analyze depth in three dimensions offers a level of insight that traditional methods may lack. As technology continues to advance, the integration of stereo measurement with other innovative techniques will likely enhance its effectiveness further.
In practical applications, industries such as mining, construction, and environmental monitoring are already reaping the benefits of this method. For instance, in mining operations, accurate pit depth measurements can lead to more efficient resource extraction and better planning of operations. In construction, understanding the depth of excavations can prevent costly mistakes and ensure safety compliance. Environmental monitoring also benefits, as accurate depth readings can help assess the impact of human activities on natural landscapes.
The future of stereo measurement in reading pit depth appears promising. As researchers and practitioners continue to refine the techniques and address the challenges, the accuracy and reliability of this method will only improve. The ongoing development of software and hardware solutions will further enhance the capabilities of stereo measurement, making it an indispensable tool in various fields.
Ultimately, the question of whether stereo measurement can effectively read pit depth is answered with a resounding yes. Its ability to provide detailed, accurate, and comprehensive data makes it a valuable asset in the toolkit of modern measurement techniques. As industries continue to evolve and demand greater precision, stereo measurement will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of surveying and analysis.



